Abstract
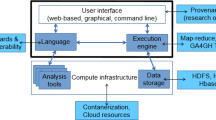
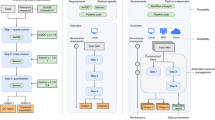
Reproducibility, resilience, and large-scale data processing have become fundamental for developing scientific research, particularly in bioinformatics. One may consider the use of Scientific Workflow Management Systems (SWfMS) to address these topics. However, user interactivity during the execution of workflows, especially with a preliminary result generated by an inner workflow task, is still an issue. We present in this paper an architecture that meets the interactive requirements of these systems, allowing the development of a flexible layer for end users to interact directly with SWfMS. Besides presenting our software solution, we show an application in the context of cancer gene identification for drug design.
Supported by the Brazilian Science and Technology Ministery and by CAPES Funding Agency.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Prefect architecture: https://docs.prefect.io/orchestration/server/architecture.html.
References
Albrecht, J.: How the GDPR will change the world. Eur. Data Prot. Law Rev. 2(3), 287–289 (2017). https://doi.org/10.21552/edpl/2016/3/4
Altintas, I., Berkley, C., Jaeger, E., Jones, M., Ludäscher, B., Mock, S.: Kepler: an extensible system for design and execution of scientific workflows. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Scientific and Statistical Database Management, SSDBM, vol. 16, pp. 423–424 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/ssdm.2004.1311241
Barker, A., van Hemert, J.: Scientific workflow: a survey and research directions. In: Wyrzykowski, R., Dongarra, J., Karczewski, K., Wasniewski, J. (eds.) PPAM 2007. LNCS, vol. 4967, pp. 746–753. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-68111-3_78
Dagogo-Jack, I., Shaw, A.T.: Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15, 81–94 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.166
Davidson, S.B., et al.: Provenance in scientific workflow systems. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 30(4), 44–50 (2007)
DeelmanDeelman, E., et al.: Mapping abstract complex workflows onto grid environments. J. Grid Comput. 1(1), 25–39 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024000426962
Django Software Foundation: Django. https://djangoproject.com
Facebook: React js. https://reactjs.org
Franceschini, A., Franceschini, M.A., RUnit, S., biocViews Network, B.: Package ‘STRINGdb’ (2015)
Guan, Z., et al.: Grid-flow: a grid-enabled scientific workflow system with a petri-net-based interface. Concurrency Comput. Pract. Experience 18(10), 1115–1140 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.988
Keefe, D.F.: Integrating visualization and interaction research to improve scientific workflows. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 30(2), 8–13 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/MCG.2010.30
Langfelder, P., Horvath, S.: Wgcna: an r package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinf. 9(1), 1–13 (2008)
Laraway, S., Snycerski, S., Pradhan, S., Huitema, B.E.: An overview of scientific reproducibility: consideration of relevant issues for behavior science/analysis. Perspect. Behav. Sci. 42(1), 33–57 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40614-019-00193-3
Liu, J., Wilson, A., Gunning, D.: Workflow-based human-in-the-loop data analytics. In: ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, pp. 49–52 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1145/2609876.2609888
McPhillips, T., Bowers, S., Zinn, D., Ludäscher, B.: Scientific workflow design for mere mortals. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 25(5), 541–551 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2008.06.013
Mohammed, Y., et al.: PeptidePicker: a scientific workflow with web interface for selecting appropriate peptides for targeted proteomics experiments. J. Proteomics 106, 151–161 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2014.04.018
Newsletter, F.: What Is Negative Engineering? (2022). https://future.com/negative-engineering-and-the-art-of-failing-successfully
Pinney, J.W., Westhead, D.R.: Betweenness-based decomposition methods for social and biological networks. Interdis. Stat. Bioinf. 25, 87–90 (2006)
Prefect Technologies Inc: Prefect. https://www.prefect.io
Rahman, S., Kandogan, E.: Characterizing practices, limitations, and opportunities related to text information extraction workflows: a human-in-the-loop perspective. In: Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), pp. 1–15 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3491102.3502068
Shannon, P., et al.: Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13(11), 2498–2504 (2003)
Smoot, M.E., Ono, K., Ruscheinski, J., Wang, P.L., Ideker, T.: Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 27(3), 431–432 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq675
Tsimberidou, A.M., Fountzilas, E., Nikanjam, M., Kurzrock, R.: Review of precision cancer medicine: evolution of the treatment paradigm. Cancer Treat. Rev. 86, 102019 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102019
Van Rossum, G., Drake, F.L.: Python 3 Reference Manual. CreateSpace, Scotts Valley (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vieira, D.M., Heine, A., de Armas, E.M., de Lanna, C.A., Boroni, M., Lifschitz, S. (2022). Scientific Workflow Interactions: An Application to Cancer Gene Identification. In: Scherer, N.M., de Melo-Minardi, R.C. (eds) Advances in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology. BSB 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13523. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21175-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21175-1_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-21174-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-21175-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)